


Let’s quickly look at some common business intelligence applications : Spreadsheets BI helps employees obtain a simple summary of a business’s tracking and address areas of opportunity and concern.īI software and tools come in a variety of forms.
These data sets are then analyzed and the findings are presented on dashboards and in reports. An organization’s Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and other data sets feed data to the software using Application Programming Interface (API) or sync tools. Business intelligence applications can solve such problems by analyzing current data to present on a quick-metrics dashboard designed to facilitate good decisions.īusiness intelligence software can convert vast volumes of data into compressed insights for informed decision-making. Dashboards also consolidate and streamline the time and effort required to search, query or merge the data.īusiness intelligence examples tell us that the idea behind its need is that, on average, managers will make poor decisions due to incomplete or inaccurate information, which may not happen if the information is better. Dashboards allow us to examine data and understand trends by looking at underlying details. At the core of BI lies reporting, with dashboards acting as standard tools for providing concise summaries. It’s a suite of services and software that transforms data into actionable knowledge and information. What Is The Modern Definition Of Business Intelligence?īusiness intelligence (BI) is a set of architectures, technologies and processes that can drive profitable business actions by converting raw data into vital information.
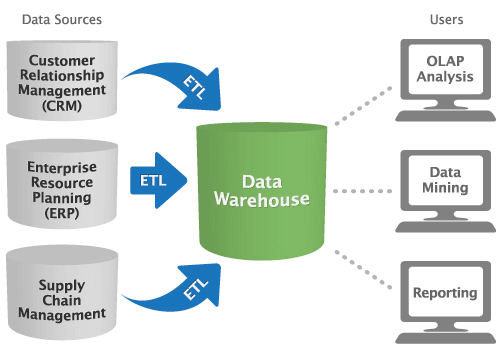
Soon it became a specific offering from BI teams with service solutions that relied on IT. It developed further for decision-making, turning data into insights. Business intelligence emerged as an information-sharing system across an organization in the 1960s.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
